Union Navy Officer Ranks in the Civil War
At the beginning of the Civil War the expected progression of regular naval officers through the commissioned ranks was as follows:

For example:

An officer who commanded a squadron could be called a flag officer, but that was a billet and not a rank.
When the war began there was a huge demand for temporary (for the duration of the war) volunteer officers for the rapidly increasing Union fleet. The Navy Department appointed acting officers:
- Former naval officers could be appointed Acting Lieutenants.
- Men with naval experience but who had not been officers could be appointed Acting Volunteer Lieutenants.
- Men with some naval or at least nautical experience could be appointed Acting Masters.
- Men with no naval or nautical experience at all could be appointed Acting Master’s Mates. An acting master’s mate was considered the equivalent of a midshipman, but the latter always took precedence over an acting master’s mate, since a midshipman would have had a lot more naval experience.
The officer rank of acting master’s mate could be confused with the enlisted rating of master’s mate. An “acting master’s mate” was the lowest commissioned rank in the volunteer Navy, but a simple “master’s mate” was a high-level enlisted rating.
Midshipmen, passed midshipmen (usually), and acting master’s mates were considered steerage officers. Other steerage officers included boatswains, gunners, carpenters, sailmakers, 2nd and 3rd assistant engineers, and clerks. Masters and higher ranking officers, chief engineers, paymasters, and surgeons were considered wardroom officers, who had better quarters than steerage officers.
In July 1862 the naval ranks were changed. Thereafter the expected progression was as follows:
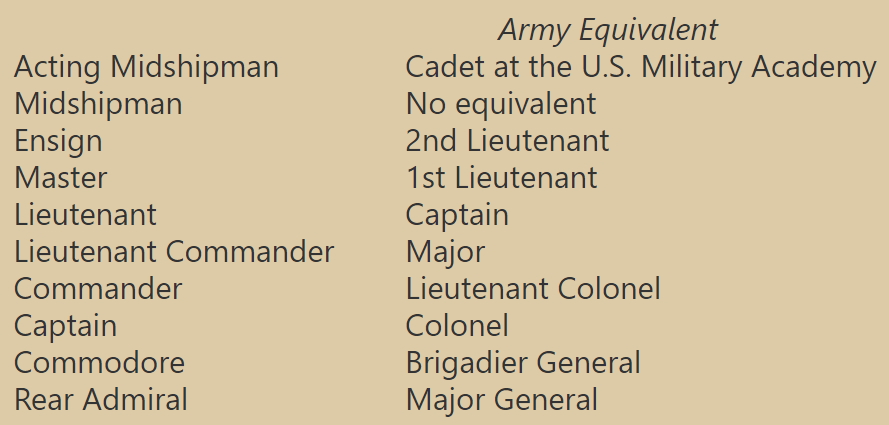
An ensign could be either a steerage officer or a wardroom officer depending on duties, such as watch and division assignments. Presumably the same applied to passed midshipmen, the rank which was replaced by ensign.
The designation of flag officer was replaced by the commodore and rear admiral ranks.
In January 1865 the rank of vice admiral (equivalent to an Army lieutenant general) was created for David Farragut.
The Confederate States Navy had similar ranks.
In 1883 the rank of master was replaced by that of lieutenant, junior grade (Lt., j.g.)
In 1912 graduates of the Naval Academy were commissioned directly as ensigns, and cadets were called midshipmen.
In 1985 the rank of commodore was replaced by rear admiral (lower half).